Topic: Atom And The Ion
Atom And The Ion
When an F atom becomes an F− ion, the F atom
(1) gains a proton
(2) loses a proton
(3) gains an electron
(4) loses an electron
When a Mg2+ ion becomes a Mg atom, the radius increases because the Mg2+ ion
(1) gains 2 protons
(2) gains 2 electrons
(3) loses 2 protons
(4) loses 2 electrons
A magnesium atom that loses two electrons becomes a
(1) positive ion with a smaller radius
(2) negative ion with a smaller radius
(3) positive ion with a larger radius
(4) negative ion with a larger radius
Compared to a potassium atom, a potassium ion has
(1) a smaller radius
(2) a larger radius
(3) fewer protons
(4) more protons
What occurs when a magnesium atom becomes a magnesium ion?
(1) Electrons are gained and the oxidation number increases.
(2) Electrons are gained and the oxidation number decreases.
(3) Electrons are lost and the oxidation number increases.
(4) Electrons are lost and the oxidation number decreases.
Solid sodium chloride, also known as table salt, can be obtained by the solar evaporation of seawater and from underground mining. Liquid sodium chloride can be decomposed by electrolysis to produce liquid sodium and chlorine gas, as represented by the equation below.
2NaCl(ℓ) → 2Na(ℓ) + Cl2(g)
State, in terms of electrons, why the radius of a Na+ ion in the table salt is smaller than the radius of a Na atom.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The Na atom is formed when the Na+ ion gains an electron.
• A Na+ ion has 10 electrons and a Na atom has 11 electrons.
• A sodium atom has one more electron shell than a sodium ion.
• A Na+ ion is formed when a Na atom loses an electron.
• Note: Do not allow credit for a response indicating that the sodium ion lost an electron.
A bottled water label lists the ions dissolved in the water. The table below lists the mass of some ions dissolved in a 500.-gram sample of the bottled water.
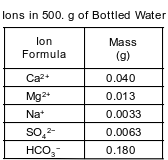
Compare the radius of a Mg2+ ion to the radius of a Mg atom.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The Mg2+ ion has a smaller radius than an Mg atom.
• The Mg atom is larger.
The formulas and names of four chloride compounds are shown in the table below.
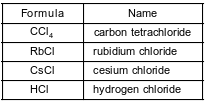
Explain, in terms of atomic structure, why the radius of a cesium ion in cesium chloride is smaller than the radius of a cesium atom when both are in the ground state.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• A cesium atom loses its valence electron, making the cesium ion smaller.
• The cesium atom has one more electron shell than the cesium ion.
• A Cs+ ion has only 5 shells of electrons in the ground state and the Cs atom has 6 shells.
The radius of a lithium atom is 130. picometers, and the radius of a fluorine atom is 60. picometers. The radius of a lithium ion, Li+, is 59 picometers, and the radius of a fluoride ion, F−, is 133 picometers.
Compare the radius of a fluoride ion to the radius of a fluorine atom.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The radius of a fluoride ion is larger than the radius of a fluorine atom.
• The radius of F− is 73 pm greater than the radius of an F atom.
• The F atom is 60 pm, the F− is 133 pm.
• The F atom is smaller.
Potassium phosphate, K3PO4, is a source of dietary potassium found in a popular cereal. According to the Nutrition-Facts label shown on the boxes of this brand of cereal, the accepted value for a one-cup serving of this cereal is 170. milligrams of potassium. The minimum daily requirement of potassium is 3500 milligrams for an adult human.
Compare the radius of a potassium ion to the radius of a potassium atom.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The radius of a potassium ion is smaller than the radius of a potassium atom.
• The radius of the atom is greater.
• The K+ ions are smaller.
• K+ < K
A sample of seawater is analyzed. The table below gives the concentration of some ions in the sample.
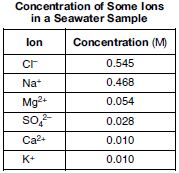
Compare the radius of an Mg2+ ion in the seawater to the radius of an Mg atom.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The radius of an Mg2+ ion is smaller than the radius of an Mg atom.
• The atom has a larger radius than the ion.
Explain, in terms of electrons, why the radius of a potassium atom is larger than the radius of a potassium ion in the ground state.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• A potassium atom has four electron shells and a potassium ion has three electron shells.
• A potassium atom has one more electron shell than a potassium ion.
• A K+ ion has one fewer electron than a K atom.
When magnesium is ignited in air, the magnesium reacts with oxygen and nitrogen. The reaction between magnesium and nitrogen is represented by the unbalanced equation below.
Mg(s) + N2(g) → Mg3N2(s)
Explain, in terms of electrons, why an atom of the metal in this reaction forms an ion that has a smaller radius than its atom.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• An atom of magnesium loses its outer shell electrons to form the Mg2+ ion.
• The electron configuration of a magnesium atom is 2-8-2, and the electron configuration of the magnesium ion is 2-8.
• An atom of the metal loses electrons to form the ion.
The atomic number and corresponding atomic radius of the Period 3 elements are shown in the data table below.
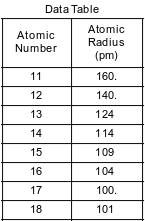
Explain, in terms of electrons, the change in radius when a sodium atom becomes a sodium ion.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The radius of a sodium ion is smaller because the sodium atom lost one electron.
• An Na+ ion is smaller because it has one fewer electron shell.
The diagram below represents an operating electrolytic cell used to plate silver onto a nickel key. As the cell operates, oxidation occurs at the silver electrode and the mass of the silver electrode decreases.
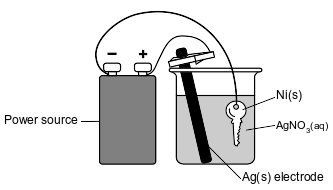
Explain, in terms of Ag atoms and Ag+(aq) ions, why the mass of the silver electrode decreases as the cell operates.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Silver atoms lose electrons and become silver ions in the solution.
• Some of the Ag atoms become Ag+ ions.
• Silver atoms are oxidized to silver ions.
