Topic: Classification Of Matter
Classification Of Matter
Which sample of matter represents a mixture?
(1) aqueous ammonia
(2) gaseous ethane
(3) liquid mercury
(4) solid iodine
Which sample of matter is classified as a substance?
(1) air
(2) ammonia
(3) milk
(4) seawater
At STP, a 50.-gram sample of H2O(ℓ) and a 100.-gram sample of H2O(ℓ) have
(1) the same chemical properties
(2) the same volume
(3) different temperatures
(4) different empirical formulas
Compared to a 15-gram sample of Cu(s) at 25°C, a 25-gram sample of Cu(s) at 25°C has
(1) the same density and the same chemical properties
(2) the same density and different chemical properties
(3) a different density and the same chemical properties
(4) a different density and different chemical properties
Which two particle diagrams each represent a sample of one substance?
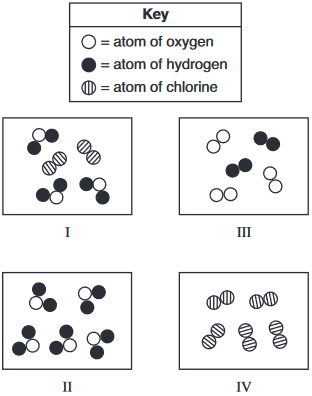
(1) I and II
(2) I and III
(3) II and III
(4) II and IV
Given the particle diagram:
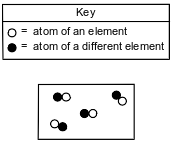
Which type of matter is represented by the particle diagram?
(1) an element
(2) a compound
(3) a homogeneous mixture
(4) a heterogeneous mixture
Given four particle models:

Which two models can be classified as elements?
(1) I and II
(2) I and IV
(3) II and III
(4) II and IV
Compared to a 26-gram sample of NaCl(s) at STP, a 52-gram sample of NaCl(s) at STP has
(1) a different density
(2) a different gram-formula mass
(3) the same chemical properties
(4) the same volume
A substance is classified as either an element or a
(1) compound
(2) solution
(3) heterogeneous mixture
(4) homogeneous mixture
At STP, which physical property of aluminum always remains the same from sample to sample?
(1) mass
(2) density
(3) length
(4) volume
Which substance can not be broken down by chemical means?
(1) aluminum
(2) ammonia
(3) aluminum oxide
(4) ammonium chloride
Nitrogen gas and oxygen gas make up about 99% of Earth’s atmosphere. Other atmospheric gases include argon, carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, hydrogen, etc.
The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can vary. Data for the concentration of CO2(g) from 1960 to 2000 are shown in the table below.

Explain why the atmosphere is classified as a mixture.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The gases in a mixture can be separated by physical means.
• The gases in the atmosphere are separate elements or compounds that are not chemically combined with each other.
• The proportions of the gases in the atmosphere can vary.
• more than one substance
In the late 19th century, the Hall-Herroult process was invented as an inexpensive way to produce aluminum. In this process, Al2O3(ℓ) extracted from bauxite is dissolved in Na3AlF6(ℓ) in a graphite-lined tank, as shown in the diagram below. The products are carbon dioxide and molten aluminum metal.
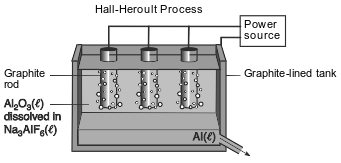
Compare the chemical properties of a 300.-kilogram sample of Al2O3(ℓ) with the chemical properties of a 600.-kilogram sample of Al2O3(ℓ).
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Both samples have the same chemical properties.
John Dalton, an early scientist, sketched the structure of compounds using his own symbols for the elements known at the time. Dalton’s symbols for four elements and his drawing of potassium aluminum sulfate are represented by the diagram below.
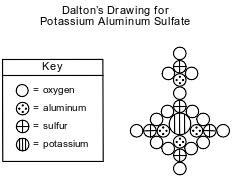
Today, it is known that the chemical formula for potassium aluminum sulfate is KAl(SO4)2•12H2O. It is a hydrated compound because water molecules are included within its crystal structure. There are 12 moles of H2O for every 1 mole of KAl(SO4)2. The compound contains two different positive ions. The gram-formula mass of KAl(SO4)2•12H2O is 474 grams per mole.
Describe, in terms of composition, one way in which Dalton’s perception of potassium aluminum sulfate differs from what is known today about the compound.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Dalton’s drawing did not include the element hydrogen.
• He perceived 5 sulfur atoms, but the formula actually has 2 sulfur atoms.
• Dalton’s drawing had more aluminum.
• It did not include water.
Iron has been used for thousands of years. In the air, iron corrodes. One reaction for the corrosion of iron is represented by the balanced equation below.
Equation 1: 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(s)
In the presence of water, iron corrodes more quickly. This corrosion is represented by the unbalanced equation below.
Equation 2: Fe(s) + O2(g) + H2O(ℓ) → Fe(OH)2(s)
Identify one substance in the passage that can not be broken down by a chemical change.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Fe
• oxygen
