Topic: Neutralization And Titration
Neutralization And Titration
In a neutralization reaction, an aqueous solution of an Arrhenius acid reacts with an aqueous solution of an Arrhenius base to produce
(1) an ether and water
(2) an ether and an alcohol
(3) a salt and water
(4) a salt and an alcohol
Which equation represents a neutralization reaction?
(1) 6HClO → 4HCl + 2HClO3
(2) CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
(3) Ca(OH)2 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2H2O
(4) Ba(OH)2 + Cu(NO3)2 → Ba(NO3)2 + Cu(OH)2
Which type of reaction occurs when an Arrhenius acid reacts with an Arrhenius base to form a salt and water?
(1) combustion
(2) decomposition
(3) neutralization
(4) saponification
Which equation represents neutralization?
(1) 6Li(s) + N2(g) → 2Li3N(s)
(2) 2Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2MgO(s)
(3) 2KOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → K2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(ℓ)
(4) Pb(NO3)2(aq) + K2CrO4(aq) → 2KNO3(aq) + PbCrO4(s)
Which type of reaction occurs when H+(aq) reacts with OH−(aq)?
(1) combustion
(2) decomposition
(3) fermentation
(4) neutralization
Which acid and base react to form water and sodium sulfate?
(1) sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide
(2) sulfuric acid and potassium hydroxide
(3) sulfurous acid and sodium hydroxide
(4) sulfurous acid and potassium hydroxide
The reaction of an Arrhenius acid with an Arrhenius base produces water and
(1) a salt
(2) an ester
(3) an aldehyde
(4) a halocarbon
What are the products when potassium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid?
(1) KH(s), Cl+(aq), and OH−(aq)
(2) K(s), Cl2(g), and H2O(ℓ)
(3) KCl(aq) and H2O(ℓ)
(4) KOH(aq) and Cl2(g)
In a titration, 10.0 mL of 0.0750 M HCl(aq) is exactly neutralized by 30.0 mL of KOH(aq) of unknown concentration. What
is the concentration of the KOH(aq) solution?
(1) 0.0250 M
(2) 0.0750 M
(3) 0.225 M
(4) 0.333 M
The gastric juice of the human stomach has a pH value of approximately 1.5. Hydrochloric acid in the gastric juice is necessary for the digestion process. However, excess hydrochloric acid may harm the stomach lining. One type of antacid uses Mg(OH)2(s) to neutralize excess hydrochloric acid in the stomach. This neutralization is represented by the incomplete equation below.
Mg(OH)2(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ___ (aq) + 2H2O(ℓ)
Complete the equation below by writing the formula of the missing product.

Allow 1 credit for MgCl2(aq).
During a laboratory activity, a student places 25.0 mL of HCl(aq) of unknown concentration into a flask. The student adds four drops of phenolphthalein to the solution in the flask. The solution is titrated with 0.150 M KOH(aq) until the solution appears faint pink. The volume of KOH(aq) added is 18.5 mL.
Complete the equation in your answer booklet for the neutralization reaction that occurs during the titration.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• KCl(aq) + H2O(ℓ)
• K+ + Cl− + OH2(ℓ)
• HOH + ClK
In a titration, 50.0 milliliters of 0.026 M HCl(aq) is neutralized by 38.5 milliliters of KOH(aq).
Complete the equation below for the neutralization by writing the formula of the missing product.

Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• KCl
• ClK
• K+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
• K+ + Cl−
In a titration, 20.0 milliliters of 0.15 M HCl(aq) is exactly neutralized by 18.0 milliliters of KOH(aq).
Complete the equation below for the neutralization reaction by writing the formula of each product.
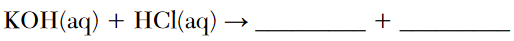
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• H2O(ℓ ) and KCl(aq)
• KCl and HOH
In a titration, a few drops of an indicator are added to a flask containing 35.0 milliliters of HNO3(aq) of unknown concentration. After 30.0 milliliters of 0.15 M NaOH(aq) solution is slowly added to the flask, the indicator changes color, showing the acid is neutralized.
Complete the equation for this neutralization reaction by writing the formula of each product.
HNO3(aq) + NaOH(aq) → ____________________ + ____________________
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• NaNO3(aq) + H2O(ℓ )
• HOH + NaNO3
A NaOH(aq) solution with a pH value of 13 is used to determine the molarity of a HCl(aq) solution. A 10.0-mL sample of the HCl(aq) is exactly neutralized by 16.0 mL of 0.100 M NaOH(aq). During this laboratory activity, appropriate safety equipment was used and safety procedures were followed.
Determine the molarity of the HCl(aq) sample, using the titration data.
Allow 1 credit for 0.160 M or .16 M.
