Topic: Nuclear Chemistry
Nuclear Chemistry
What evidence indicates that the nuclei of strontium-90 atoms are unstable?
(1) Strontium-90 electrons are in the excited state.
(2) Strontium-90 electrons are in the ground state.
(3) Strontium-90 atoms spontaneously absorb beta particles.
(4) Strontium-90 atoms spontaneously emit beta particles.
The stability of an isotope is related to its ratio of
(1) neutrons to positrons
(2) neutrons to protons
(3) electrons to positrons
(4) electrons to protons
The stability of isotopes is related to the ratio of which particles in the atoms?
(1) electrons and protons
(2) electrons and positrons
(3) neutrons and protons
(4) neutrons and positrons
Which statement describes the stability of the nuclei of potassium atoms?
(1) All potassium atoms have stable nuclei that spontaneously decay.
(2) All potassium atoms have unstable nuclei that do not spontaneously decay.
(3) Some potassium atoms have unstable nuclei that spontaneously decay.
(4) Some potassium atoms have unstable nuclei that do not spontaneously decay.
Radiation is spontaneously emitted from hydrogen-3 nuclei, but radiation is not spontaneously emitted from hydrogen-1 nuclei or hydrogen-2 nuclei. Which hydrogen nuclei are stable?
(1) nuclei of H-1 and H-2, only
(2) nuclei of H-1 and H-3, only
(3) nuclei of H-2 and H-3, only
(4) nuclei of H-1, H-2, and H-3
Nuclei of U-238 atoms are
(1) stable and spontaneously absorb alpha particles
(2) stable and spontaneously emit alpha particles
(3) unstable and spontaneously absorb alpha particles
(4) unstable and spontaneously emit alpha particles
Based on Table N, uranium-238 and uranium-235 have different
(1) decay modes
(2) half-lives
(3) numbers of protons
(4) numbers of electrons
What is the mass of an original 5.60-gram sample of iron-53 that remains unchanged after 25.53 minutes?
(1) 0.35 g
(2) 0.70 g
(3) 1.40 g
(4) 2.80 g
Which radioisotope has the fastest rate of decay?
(1) 14C
(2) 37Ca
(3) 53Fe
(4) 42K
Which phrase describes the decay modes and the half-lives of K-37 and K-42?
(1) the same decay mode but different half-lives
(2) the same decay mode and the same half-life
(3) different decay modes and different half-lives
(4) different decay modes but the same half-life
A radioactive isotope has a half-life of 2.5 years. Which fraction of the original mass remains unchanged after 10. years?
(1) 1/2
(2) 1/4
(3) 1/8
(4) 1/16
Phosphorus-30 and phosphorus-32 are radioisotopes. Phosphorus-30 decays by positron emission.
Based on Table N, determine the time required for an original 100.-milligram sample of P-32 to decay until only 25 milligrams of the sample remain unchanged.
Allow 1 credit for 28.56 d. Significant figures do not need to be shown.
Radioactive emissions can be detected by a Geiger counter. When radioactive emissions enter the Geiger counter probe, which contains a noble gas such as argon or helium, some of the atoms are ionized. The ionized gas allows for a brief electric current. The current causes the speaker to make a clicking sound. To make sure that the Geiger counter is measuring radiation properly, the device is tested using the radioisotope Cs-137.
To detect gamma radiation, an aluminum shield can be placed over the probe window, to keep alpha and beta radiation from entering the probe. A diagram that represents the Geiger counter is shown below.
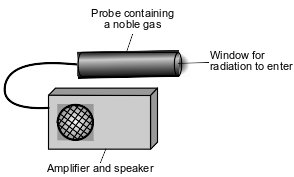
Determine the time required for a sample of cesium-137 to decay until only 1/8 of the original sample remains unchanged.
Allow 1 credit for 90.6 y. Significant figures do not need to be shown.
Cobalt-60 is an artifi cial isotope of Co-59. The incomplete equation for the decay of cobalt-60, including beta and gamma emissions, is shown below.
![]()
Based on Table N, determine the total time required for an 80.00-gram sample of cobalt-60 to decay until only 10.00 grams of the sample remain unchanged.
Allow 1 credit for 15.813 y. Significant figures do not need to be shown.
In the past, some paints that glowed in the dark contained zinc sulfide and salts of Ra-226. As the radioisotope Ra-226 decayed, the energy released caused the zinc sulfide in these paints to emit light. The half-lives for Ra-226 and two other radioisotopes used in these paints are listed on the table below.
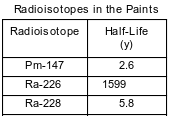
What fraction of an original Ra-228 sample remains unchanged after 17.4 years?
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• 1/8
• 0.125
• 12.5%
