Topic: Oxidation Numbers (States)
Oxidation Numbers (States)
Given the equation representing a reaction:
2Ca(s) + O2(g) → 2CaO(s)
During this reaction, each element changes in
(1) atomic number
(2) oxidation number
(3) number of protons per atom
(4) number of neutrons per atom
Given the equation representing a reaction:
3CuCl2(aq) + 2Al(s) → 3Cu(s) + 2AlCl3(aq)
The oxidation number of copper changes from
(1) +1 to 0
(2) +2 to 0
(3) +2 to +1
(4) +6 to +3
What are the two oxidation states of nitrogen in NH4NO2?
(1) +3 and +5
(2) +3 and −5
(3) −3 and +3
(4) −3 and −3
Which value changes when a Cu atom becomes a Cu2+ ion?
(1) mass number
(2) oxidation number
(3) number of protons
(4) number of neutrons
Given the equation representing a system at equilibrium:
PCl5(g) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
Which statement describes this system?
(1) The concentration of PCl5(g) is increasing.
(2) The concentration of PCl5(g) is decreasing.
(3) The concentrations of PCl5(g) and PCl3(g) are equal.
(4) The concentrations of PCl5(g) and PCl3(g) are constant.
What is the oxidation state for a Mn atom?
(1) 0
(2) +7
(3) +3
(4) +4
In a laboratory investigation, a student constructs an electrochemical cell to decompose water, as represented in the diagram below. The water in the electrochemical cell contains a small amount of dissolved sodium sulfate, to increase conductivity. The three equations represent the reaction in each test tube and the overall reaction. During this laboratory activity, appropriate safety equipment is used and safety procedures are followed.
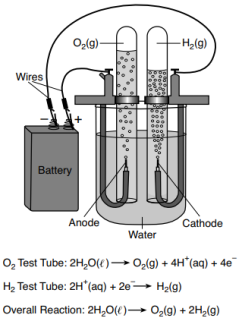
State the change in oxidation number that occurs for oxygen in the overall reaction.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• From −2 to 0
• From 2− to 0
• From negative two to zero
• Note: Do not allow credit for 2 without a minus sign (−).
Fuel cells are voltaic cells. In one type of fuel cell, oxygen gas, O2(g), reacts with hydrogen gas, H2(g), producing water vapor, H2O(g), and electrical energy. The unbalanced equation for this redox reaction is shown below.
H2(g) + O2(g) → H2O(g) + energy
A diagram of the fuel cell is shown below. During operation of the fuel cell, hydrogen gas is pumped into one compartment and oxygen gas is pumped into the other compartment. Each compartment has an inner wall that is a porous carbon electrode through which ions flow. Aqueous potassium hydroxide, KOH(aq), and the porous electrodes serve as the salt bridge.
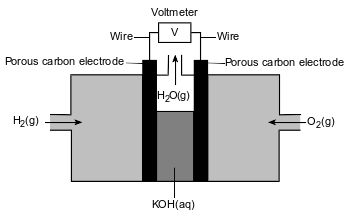
Determine the change in oxidation number for oxygen in this operating fuel cell.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• From 0 to −2
• From 0 to 2−
• From zero to negative 2
Nitrogen dioxide, NO2, is a dark brown gas that is used to make nitric acid and to bleach flour. Nitrogen dioxide has a boiling point of 294 K at 101.3 kPa. In a rigid cylinder with a movable piston, nitrogen dioxide can be in equilibrium with colorless dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4. This equilibrium is represented by the equation below.
2NO2(g) ⇌ N2O4(g) + 58 kJ
Determine the oxidation state of nitrogen in nitrogen dioxide.
Allow 1 credit for +4 or 4+ or four.
The electrolysis of brine, a concentrated aqueous sodium chloride solution, produces three important industrial chemicals: chlorine gas, hydrogen gas, and sodium hydroxide. The diagram and equation below represent a brine electrolysis cell. Before the battery is connected, the pH value of the brine solution is 7.0.
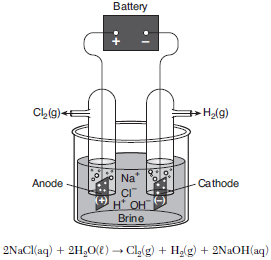
State the oxidation number of oxygen in the aqueous product.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• −2
• 2−
• negative two
The diagram and balanced ionic equation below represent two half-cells connected to produce an operating voltaic cell in a laboratory investigation. The half-cells are connected by a salt bridge.
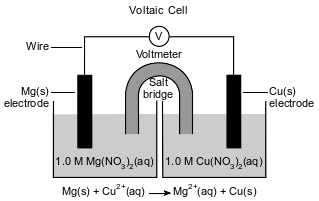
Determine the oxidation number of nitrogen in the negative ion in the aqueous solutions.
Allow 1 credit for +5 or 5 or five.
One type of voltaic cell, called a mercury battery, uses zinc and mercury(II) oxide to generate an electric current. Mercury batteries were used because of their miniature size, even though mercury is toxic. The overall reaction for a mercury battery is given in the equation below.
Zn(s) + HgO(s) → ZnO(s) + Hg(ℓ)
Determine the change in the oxidation number of zinc during the operation of the cell.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• From 0 to +2
• From 0 to 2+
• From zero to two
Fossil fuels produce air pollution and may eventually be depleted. Scientists are researching ways to use hydrogen as an alternate fuel.
A device called an artificial leaf was invented to produce hydrogen and oxygen using sunlight and water. The artifical leaf is an electrochemical cell. Equations 1 and 2 below represent the reactions taking place in the leaf. Equation 3 represents a reaction of hydrogen when used as fuel.
Equation 1: 2H2O + energy from sunlight → O2 + 4H+ + 4e−
Equation 2: 4H+ + 4e− → 2H2
Equation 3: 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g) + energy
State the change in oxidation number of oxygen during the reaction represented in equation 3.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• From 0 to −2
• From 0 to 2−
• From zero to negative two
Early scientists defined oxidation as a chemical reaction in which oxygen combined with another element to produce an oxide of the element. An example of oxidation based on this definition is the combustion of methane. This reaction is represented by the balanced equation below.
Equation 1: CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
The definition of oxidation has since been expanded to include many reactions that do not involve oxygen. An example of oxidation based on this expanded definition is the reaction between magnesium ribbon and powdered sulfur when heated in a crucible. This reaction is represented by the balanced equation below.
Equation 2: Mg(s) + S(s) → MgS(s)
Determine the change in oxidation number of carbon in equation 1.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• from −4 to +4
• from negative four to four
The nuts, bolts, and hinges that attach some gates to a playground fence can be made of iron. The iron can react with oxygen in the air. The unbalanced equation representing this reaction is shown below.
Fe(s) + O2(g) → Fe2O3(s)
Determine the change in oxidation state for oxygen in this reaction.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• From 0 to −2
• From 0 to 2−
• From zero to negative two
