Topic: Polar Bond Polar Molecules.
Polar Bond Polar Molecules.
Which formula represents an asymmetrical molecule?
(1) CH4
(2) CO2
(3) N2
(4) NH3
Which statement describes the charge distribution and the polarity of a CH4 molecule?
(1) The charge distribution is symmetrical and the molecule is nonpolar.
(2) The charge distribution is asymmetrical and the molecule is nonpolar.
(3) The charge distribution is symmetrical and the molecule is polar.
(4) The charge distribution is asymmetrical and the molecule is polar.
Which phrase describes the molecular polarity and distribution of charge in a molecule of carbon dioxide, CO2?
(1) polar and symmetrical
(2) polar and asymmetrical
(3) nonpolar and symmetrical
(4) nonpolar and asymmetrical
Given the formula representing a molecule:
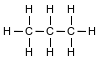
Which statement explains why the molecule is nonpolar?
(1) Electrons are shared between the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms.
(2) Electrons are transferred from the carbon atoms to the hydrogen atoms.
(3) The distribution of charge in the molecule is symmetrical.
(4) The distribution of charge in the molecule is asymmetrical.
Which substance has nonpolar covalent bonds?
(1) Cl2
(2) SO3
(3) SiO2
(4) CCl4
A molecule must be nonpolar if the molecule
(1) is linear
(2) is neutral
(3) has ionic and covalent bonding
(4) has a symmetrical charge distribution
Which formula represents a polar molecule?
(1) O2
(2) CO2
(3) NH3
(4) CH4
Which formula represents a nonpolar molecule containing polar covalent bonds?
(1) ![]()
(2) ![]()
(3) ![]()
(4) ![]()
Which statement explains why a CO2 molecule is nonpolar?
(1) Carbon and oxygen are both nonmetals.
(2) Carbon and oxygen have different electronegativities.
(3) The molecule has a symmetrical distribution of charge.
(4) The molecule has an asymmetrical distribution of charge.
Which phrase describes a molecule of CH4, in terms of molecular polarity and distribution of charge?
(1) polar with an asymmetrical distribution of charge
(2) polar with a symmetrical distribution of charge
(3) nonpolar with an asymmetrical distribution of charge
(4) nonpolar with a symmetrical distribution of charge
Which statement explains why a molecule of CH4 is nonpolar?
(1) The bonds between the atoms in a CH4 molecule are polar.
(2) The bonds between the atoms in a CH4 molecule are ionic.
(3) The geometric shape of a CH4 molecule distributes the charges symmetrically.
(4) The geometric shape of a CH4 molecule distributes the charges asymmetrically.
Which phrase describes the distribution of charge and the polarity of a CH4 molecule?
(1) symmetrical and polar
(2) symmetrical and nonpolar
(3) asymmetrical and polar
(4) asymmetrical and nonpolar
The formulas and names of four chloride compounds are shown in the table below.
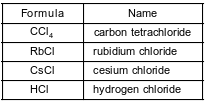
Explain, in terms of charge distribution, why a molecule of carbon tetrachloride is a nonpolar molecule.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The molecule is nonpolar because it has a symmetrical charge distribution.
• The center of positive and negative charges coincide.
The formula below represents a molecule of butanamide.
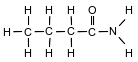
Explain, in terms of charge distribution, why a molecule of butanamide is polar.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The butanamide molecule has an asymmetrical distribution of charge.
• The molecule has an unequal charge distribution.
The Lewis electron-dot diagrams for three substances are shown below.
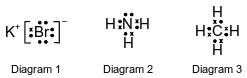
Explain, in terms of distribution of charge, why a molecule of the substance represented in diagram 3 is nonpolar.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Charge is symmetrically distributed.
• The molecule has uniform charge distribution.
• The centers of positive charge and negative charge coincide.
