Topic: Solutions
Solutions
Based on Table F, which equation represents a saturated solution having the lowest concentration of Cl− ions?
(1) NaCl(s) ⇌ Na+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
(2) AgCl(s) ⇌ Ag+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
(3) NH4Cl(s) ⇌ NH4+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
(4) KCl(s) ⇌ K+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
According to Table G, which substance forms an unsaturated solution when 80. grams of the substance are stirred into 100. grams of H2O at 10.°C?
(1) KNO3
(2) KI
(3) NH3
(4) NaCl
According to Table F, which substance is most soluble in water?
(1) AgCl
(2) CaCO3
(3) Na2CO3
(4) SrSO4
Based on Table F, which compound is least soluble in water?
(1) AlPO4
(2) Li2SO4
(3) Ca(OH)2
(4) AgC2H3O2
Which substance is most soluble in water?
(1) (NH4)3PO4
(2) Cu(OH)2
(3) Ag2SO4
(4) CaCO3
Water, H2O, and hexane, C6H14, are commonly used as laboratory solvents because they have different physical properties and are able to dissolve different types of solutes. Some physical properties of water and hexane are listed on the table below.
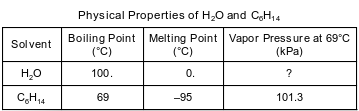
Determine the vapor pressure of water at 69°C.
Allow 1 credit for any value from 28 kPa to 30. kPa, inclusive.
A sample of normal rainwater has a pH value of 5.6 due to dissolved carbon dioxide gas from the atmosphere. Acid rain is formed when other gases, such as sulfur dioxide, dissolve in rainwater, which can result in lake water with a pH value of 4.6. The equation below represents the reaction of water with SO2(g).
![]()
Based on Table G, describe what happens to the solubility of SO2(g) as the temperature increases from 10.°C to 30.°C at standard pressure.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• As the water temperature increases, the solubility of sulfur dioxide decreases.
• The solubility of SO2 decreases.
• The SO2(g) becomes less soluble.
A 100.-gram sample of liquid water is heated from 20.0°C to 50.0°C. Enough KClO3(s) is dissolved in the sample of water at 50.0°C to form a saturated solution.
Based on Table G, determine the mass of KClO3(s) that must dissolve to make a saturated solution in 100. g of H2O at 50.0°C.
Allow 1 credit for any value from 20. g to 23 g, inclusive.
A bottled water label lists the ions dissolved in the water. The table below lists the mass of some ions dissolved in a 500.-gram sample of the bottled water.
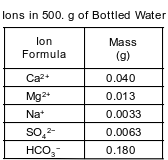
Based on Table F, write the formula of the ion in the bottled water table that would form the least soluble compound when combined with the sulfate ion.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Ca2+
• Ca+2
• Note: Do not allow credit for Ca or calcium.
At 23°C, 85.0 grams of NaNO3(s) are dissolved in 100. grams of H2O(ℓ).
Based on Table G, determine the additional mass of NaNO3(s) that must be dissolved to saturate the solution at 23°C.
Allow 1 credit for any value from 4.0 g to 6.0 g, inclusive.
In a laboratory investigation, a student is given a sample that is a mixture of 3.0 grams of NaCl(s) and 4.0 grams of sand, which is mostly SiO2(s). The purpose of the investigation is to separate and recover the compounds in the sample. In the first step, the student places the sample in a 250-mL flask. Then, 50. grams of distilled water are added to the flask, and the contents are thoroughly stirred. The mixture in the flask is then filtered, using the equipment represented by the diagram below.
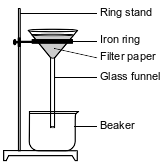
Based on Table G, state evidence that all of the NaCl(s) in the flask would dissolve in the distilled water at 20.°C.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• According to Table G, the salt solution is unsaturated.
• The 3.0 g of salt dissolved in 50. g of H2O has a concentration less than the solubility of NaCl on Table G at 20.°C.
• Table G indicates that the solubility of NaCl is greater than the amount in the sample.
A saturated solution of sulfur dioxide is prepared by dissolving SO2(g) in 100. g of water at 10.°C and standard pressure.
Based on Table G, state the general relationship between solubility and temperature of an aqueous SO2 solution at standard pressure.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The solubility at 1 atm increases as the temperature decreases.
• As the temperature of the solution increases, the solubility of SO2 decreases.
• At lower temperatures, more SO2 can dissolve.
Carbon dioxide is slightly soluble in seawater. As carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere increase, more CO2 dissolves in seawater, making the seawater more acidic because carbonic acid, H2CO3(aq), is formed.
Seawater also contains aqueous calcium carbonate, CaCO3(aq), which is used by some marine organisms to make their hard exoskeletons. As the acidity of the sea water changes, the solubility of CaCO3 also changes, as shown in the graph below.
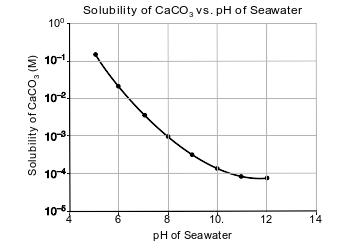
State the trend in the solubility of CaCO3 as seawater becomes more acidic.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• As the seawater becomes more acidic, the solubility of CaCO3 increases.
• As the pH of the seawater decreases, the solubility of calcium carbonate increases.
• solubility increases
• more soluble
Some compounds of silver are listed with their chemical formulas in the table below.
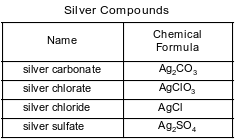
Identify the silver compound in the table that is most soluble in water.
Allow 1 credit for AgClO3 or silver chlorate.
A solution is made by dissolving 70.0 grams of KNO3(s) in 100. grams of water at 50.°C and standard pressure.
Determine the number of additional grams of KNO3 that must dissolve to make this solution saturated.
Allow 1 credit for any value from 12 g to 16 g, inclusive.
