Topic: Electrochemical Cell
Electrochemical Cell
When comparing voltaic cells to electrolytic cells, oxidation occurs at the
(1) anode in both types of cells
(2) cathode in both types of cells
(3) anode in voltaic cells, only
(4) cathode in voltaic cells, only
Which statement describes the reactions in an electrochemical cell?
(1) Oxidation occurs at the anode, and reduction occurs at the cathode.
(2) Oxidation occurs at the cathode, and reduction occurs at the anode.
(3) Oxidation and reduction both occur at the cathode.
(4) Oxidation and reduction both occur at the anode.
Which reaction occurs at the anode in an electrochemical cell?
(1) oxidation
(2) reduction
(3) combustion
(4) substitution
Which change occurs at the anode in an operating electrochemical cell?
(1) gain of protons
(2) gain of electrons
(3) loss of protons
(4) loss of electrons
Which reaction occurs at the anode of an electrochemical cell?
(1) oxidation
(2) reduction
(3) neutralization
(4) transmutation
An electrolytic cell differs from a voltaic cell because an electrolytic cell
(1) generates its own energy from a spontaneous physical reaction
(2) generates its own energy from a nonsponta- neous physical reaction
(3) requires an outside energy source for a spontaneous chemical reaction to occur
(4) requires an outside energy source for a nonspontaneous chemical reaction to occur
Where do reduction and oxidation occur in an electrolytic cell?
(1) Both occur at the anode.
(2) Both occur at the cathode.
(3) Reduction occurs at the anode, and oxidation occurs at the cathode.
(4) Reduction occurs at the cathode, and oxidation occurs at the anode.
In an operating voltaic cell, reduction occurs
(1) at the anode
(2) at the cathode
(3) in the salt bridge
(4) in the wire
At which electrode does oxidation occur in a voltaic cell and in an electrolytic cell?
(1) the anode in a voltaic cell and the cathode in an electrolytic cell
(2) the cathode in a voltaic cell and the anode in an electrolytic cell
(3) the anode in both a voltaic cell and an electrolytic cell
(4) the cathode in both a voltaic cell and an electrolytic cell
Which term identifies the half-reaction that occurs at the anode of an operating electro- chemical cell?
(1) oxidation
(2) reduction
(3) neutralization
(4) transmutation
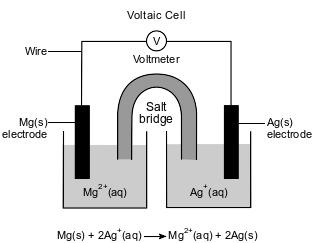
An operating voltaic cell has magnesium and silver electrodes. The cell and the ionic equation representing the reaction that occurs in the cell are shown below.
Explain, in terms of electrical energy, how electrolysis reactions differ from voltaic cell reactions.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Electrical energy is required for electrolytic reactions, while voltaic cell reactions produce electricity.
• Voltaic cells produce electrical energy, and electrolytic cells use electrical energy.
• Electrolysis reactions require an external source of electricity.
A student constructs an electrochemical cell. A diagram of the operating cell and the unbalanced ionic equation representing the reaction occurring in the cell are shown below.
The blue color of the solution in the copper half-cell indicates the presence of Cu2+ ions. The student observes that the blue color becomes less intense as the cell operates.
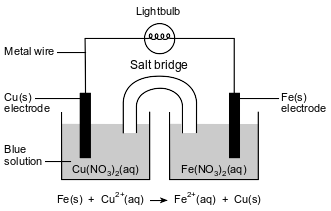
Identify the type of electrochemical cell represented by the diagram.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• voltaic cell
• voltaic
• Galvanic
The diagram and ionic equation below represent an operating voltaic cell.
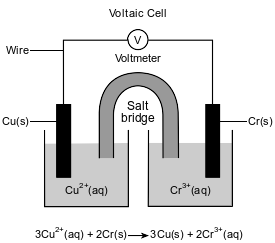
State the purpose of the salt bridge in completing the circuit in this cell.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The salt bridge allows the migration of ions between the half-cells.
• The salt bridge prevents polarization of the half-cells.
• Electrical neutrality of the solutions is maintained.
A student sets up a voltaic cell using magnesium and zinc electrodes. The porous barrier in the cell has the same purpose as a salt bridge. The diagram and the ionic equation below represent this operating cell.
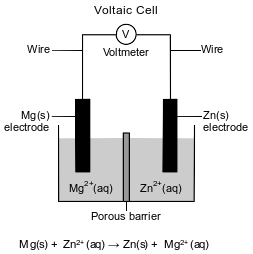
State, in terms of the relative activity of metals, why the reaction in this cell occurs.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Magnesium is more active than zinc.
• The Zn is less active than Mg.
• Mg is higher on Table J.
A student constructs an electrochemical cell during a laboratory investigation. When the switch is closed, electrons flow through the external circuit. The diagram and ionic equation below represent this cell and the reaction that occurs.
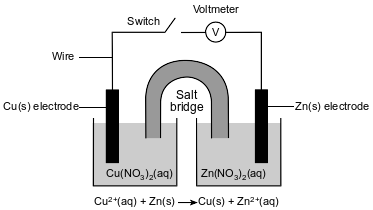
State what happens to the mass of the Cu electrode and the mass of the Zn electrode in the operating cell.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Cu electrode: mass increases. Zn electrode: mass decreases
• Cu electrode: increases. Zn electrode: decreases
