Topic: Gas Lows
Gas Lows
A rigid cylinder with a movable piston contains a sample of hydrogen gas. At 330. K, this sample has a pressure of 150. kPa and a volume of 3.50 L. What is the volume of this sample at STP?
(1) 0.233 L
(2) 1.96 L
(3) 4.29 L
(4) 6.26 L
A sample of a gas in a rigid cylinder with a movable piston has a volume of 11.2 liters at STP. What is the volume of this gas at 202.6 kPa and 300. K?
(1) 5.10 L
(2) 6.15 L
(3) 22.4 L
(4) 24.6 L
A sample of gas is in a rigid cylinder with a movable piston. The pressure of the gas is kept constant. If the Kelvin temperature of the gas is doubled, the volume of the gas is
(1) halved
(2) doubled
(3) tripled
(4) unchanged
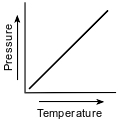
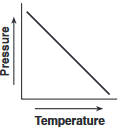
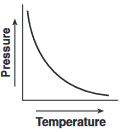
Which graph shows the relationship between pressure and Kelvin temperature for an ideal gas at constant volume?
(1) 
(2) 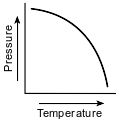
(3) 
(4) 
A sample of a gas is in a sealed, rigid container that maintains a constant volume. Which changes occur between the gas particles when the sample is heated?
(1) The frequency of collisions increases, and the force of collisions decreases.
(2) The frequency of collisions increases, and the force of collisions increases.
(3) The frequency of collisions decreases, and the force of collisions decreases.
(4) The frequency of collisions decreases, and the force of collisions increases.
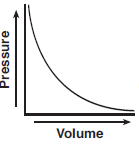
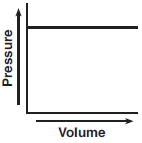
A rigid cylinder with a movable piston contains a sample of helium gas. The temperature of the gas is held constant as the piston is pulled outward. Which graph represents the relationship between the volume of the gas and the pressure of the gas?
(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
A 10.0-gram sample of nitrogen is at STP. Which property will increase when the sample is cooled to 72 K at standard pressure?
(1) mass
(2) volume
(3) density
(4) temperature
A rigid cylinder with a movable piston contains a sample of gas. At 300. K, this sample has a pressure of 240. kilopascals and a volume of 70.0 milliliters. What is the volume of this sample when the temperature is changed to 150. K and the pressure is changed to 160. kilopascals?
(1) 35.0 mL
(2) 52.5 mL
(3) 70.0 mL
(4) 105 mL
Cylinder A and cylinder B are sealed, rigid cylinders with movable pistons. Each cylinder contains 500. milliliters of a gas sample at 101.3 kPa and 298 K. Cylinder A contains H2(g) and cylinder B contains N2(g). The diagrams below represent these two cylinders.
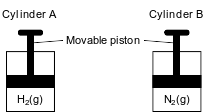
Show a numerical setup for calculating the volume of the gas in cylinder B at STP.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• ![]()
• ![]()
• ![]()
A 200.-milliliter sample of CO2(g) is placed in a sealed, rigid cylinder with a movable piston at 296 K and 101.3 kPa.
Compare the mass of the original 200.-milliliter sample of CO2(g) to the mass of the CO2(g) sample when the cylinder is adjusted to a volume of 100. milliliters.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The mass stays the same.
• Mass remains constant.
In a laboratory activity, the volume of helium gas in a rigid cylinder with a movable piston is varied by changing the temperature of the gas. The activity is done at a constant pressure of 100. kPa. Data from the activity are plotted on the graph below.
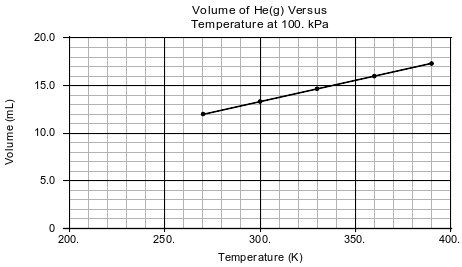
State what happens to the average distance between the He atoms as the gas is heated.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• When the temperature increases, the distance between He atoms increases.
• As the helium is heated, the He atoms move farther apart.
• The average distance increases.
A saturated solution of sulfur dioxide is prepared by dissolving SO2(g) in 100. g of water at 10.°C and standard pressure.
Describe what happens to the solubility of SO2(g) when the pressure is increased at constant temperature.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• More SO2(g) can be dissolved in water when the pressure increases.
• At higher pressure, sulfur dioxide is more soluble.
• Solubility increases.
The diagram below represents a cylinder with a moveable piston containing 16.0 g of O2(g). At 298 K and 0.500 atm, the O2(g) has a volume of 24.5 liters.
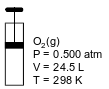
Show a numerical setup for calculating the volume of O2(g) in the cylinder at 265 K and 1.00 atm.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• 
A bubble of air at the bottom of a lake rises to the surface of the lake. Data for the air inside the bubble at the bottom of the lake and at the surface of the lake are listed in the table below.

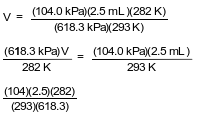
Show a numerical setup for calculating the volume of the bubble at the bottom of the lake.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• 
Ammonia, NH3(g), can be used as a substitute for fossil fuels in some internal combustion engines. The reaction between ammonia and oxygen in an engine is represented by the unbalanced equation below.
NH3(g) + O2(g) → N2(g) + H2O(g) + energy
Determine the new pressure of a 6.40-L sample of oxygen gas at 300. K and 100. kPa after the gas is compressed to 2.40 L at 900. K.
Allow 1 credit for 800. kPa. Significant figures do not need to be shown.
